As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.
In this blog post, we will explore the various types of hemorrhoids and delve into the treatment options available for both internal and external hemorrhoids.
Types and Treatment of Hemorrhoids: Internal vs. External Hemorrhoids
Introduction
Ah, hemorrhoids—those pesky little devils that can cause quite the discomfort in your rear end. But fear not, dear reader, for we are here to guide you through the ins and outs of internal and external hemorrhoids and their respective treatments. So grab a seat (preferably a cushioned one!), and let’s dive into the world of swollen veins down there.
Understanding Hemorrhoids
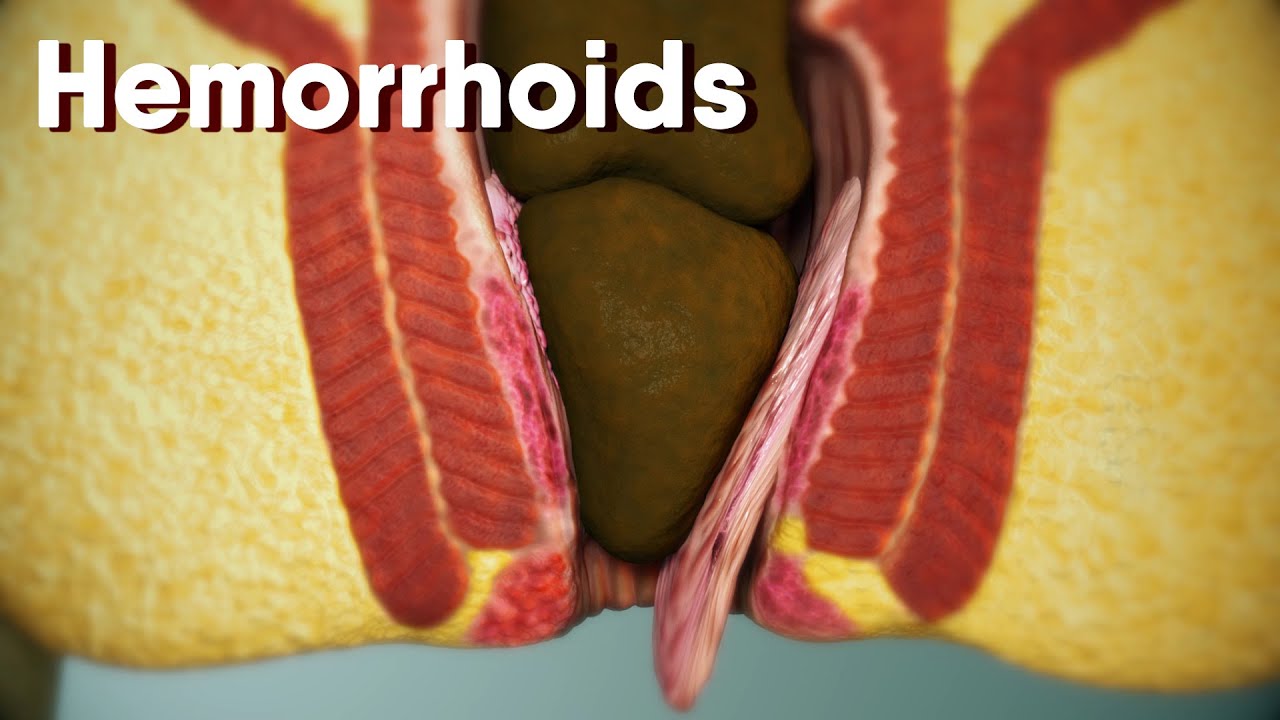
We have anal cushions in the upper anal canal with connections between rectal arteries and veins, supported by smooth muscle and tissue. When these cushions become swollen or inflamed, they give rise to hemorrhoids. Hemorrhoids can be internal or external, depending on their location relative to the dentate line, an important anatomical landmark in the anal canal.
Internal Hemorrhoids
Internal hemorrhoids are cunning little troublemakers that lurk inside the rectum above the dentate line. They are classified into four grades based on their severity and prolapse. The symptoms of internal hemorrhoids often include painless bleeding, a sensation of rectal fullness, mucous discharge, and itchiness.
Grades of Internal Hemorrhoids
- Grade I: These hemorrhoids do not prolapse and are usually painless.
- Grade II: Hemorrhoids prolapse during bowel movements but retract on their own.
- Grade III: Prolapsed hemorrhoids require manual reduction post-bowel movement.
- Grade IV: Severe prolapse of hemorrhoids that cannot be reduced and may require surgical intervention.
External Hemorrhoids
On the other hand, external hemorrhoids make their presence known outside the anal opening. They typically present as visible swelling, with pain being a significant symptom, especially if the hemorrhoid becomes thrombosed.
Causes and Risk Factors
Various factors can lead to the development of hemorrhoids, including:
- Constipation: Straining during bowel movements can put pressure on the veins in the anal area.
- Prolonged Toilet Sitting: Spending too long on the porcelain throne can contribute to hemorrhoid formation.
- Obesity: Excess weight can increase pressure on the rectal veins, leading to hemorrhoids.
- Pregnancy: The hormonal changes and increased pressure on the pelvic area during pregnancy can predispose women to hemorrhoids.
Managing and Treating Hemorrhoids
While hemorrhoids can often resolve on their own, there are ways to ease the discomfort and promote healing. Here are some tips for managing hemorrhoids:
- Topical Treatments: Over-the-counter creams, ointments, and suppositories can help soothe symptoms.
- Sitz Baths: Soaking the affected area in warm water can provide relief and reduce inflammation.
- Dietary Changes: Drinking an adequate amount of water and increasing fiber intake can prevent constipation, a common trigger for hemorrhoids.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Avoiding straining during bowel movements, maintaining good hygiene, and staying physically active can help prevent hemorrhoids.
Consulting a Healthcare Professional
If symptoms worsen or significantly impact your daily life, it is crucial to consult a doctor for a proper diagnosis and tailored treatment plan. Depending on the severity of hemorrhoids, medical interventions such as rubber band ligation, sclerotherapy, or surgery may be recommended.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the differences between internal and external hemorrhoids is key to proper management and treatment. By incorporating healthy habits, seeking medical advice when needed, and being proactive in managing symptoms, you can bid farewell to those unwelcome guests in your nether regions.
FAQs About Hemorrhoids
- What are the main differences between internal and external hemorrhoids?
- Can hemorrhoids go away on their own without any treatment?
- Are there any natural remedies that can help alleviate hemorrhoid symptoms?
- When should I consider surgery as a treatment option for hemorrhoids?
- Is it possible to prevent hemorrhoids from occurring in the first place?
Amazon and the Amazon logo are trademarks of Amazon.com, Inc, or its affiliates.