As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.
Hemorrhoids are swollen veins in your lower rectum and anus. Internal hemorrhoids develop inside the rectum and are usually painless, while external hemorrhoids form under the skin around the anus and can cause significant discomfort. You may experience bleeding, itching, or pain, depending on the type. Common causes include straining during bowel movements, pregnancy, and prolonged sitting. Your doctor can diagnose hemorrhoids through a physical exam or more advanced methods if needed. Treatment options range from home remedies to medical procedures, depending on severity. Understanding the differences between internal and external hemorrhoids can help you find the most effective solution for your specific condition.
What Are Hemorrhoids?
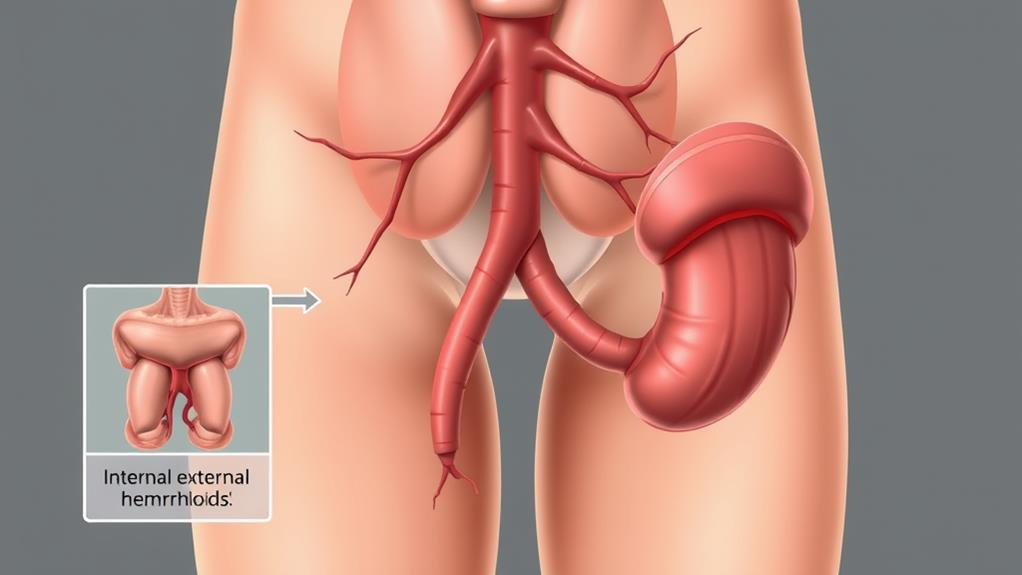
Hemorrhoids are swollen veins in the lower rectum and anus. They're a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide. You might develop hemorrhoids due to increased pressure in the lower rectum, often caused by straining during bowel movements, pregnancy, or prolonged sitting.
There are two types of hemorrhoids: internal and external. Internal hemorrhoids occur inside the rectum and are usually painless. You may not even notice them unless they bleed. External hemorrhoids, on the other hand, form under the skin around your anus. These can be more uncomfortable and may cause pain, especially when you sit or have a bowel movement.
Symptoms of hemorrhoids can vary depending on their location and severity. Common signs include rectal bleeding, anal itching, and discomfort. You might also feel a lump near your anus, which can be painful if it's an external hemorrhoid. While hemorrhoids can be bothersome, they're generally not dangerous and can often be treated with simple home remedies or over-the-counter medications. However, if you experience persistent symptoms or severe pain, it's important to consult your doctor for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Internal Hemorrhoids Explained
Internal hemorrhoids develop inside your rectum and are typically painless due to their location. You might notice bright red blood on toilet paper or in the bowl, and in more advanced cases, you may feel tissue protruding from your anus. Treatment options range from simple lifestyle changes like increasing fiber intake to medical procedures for severe cases that don't respond to conservative measures.
Location and Appearance
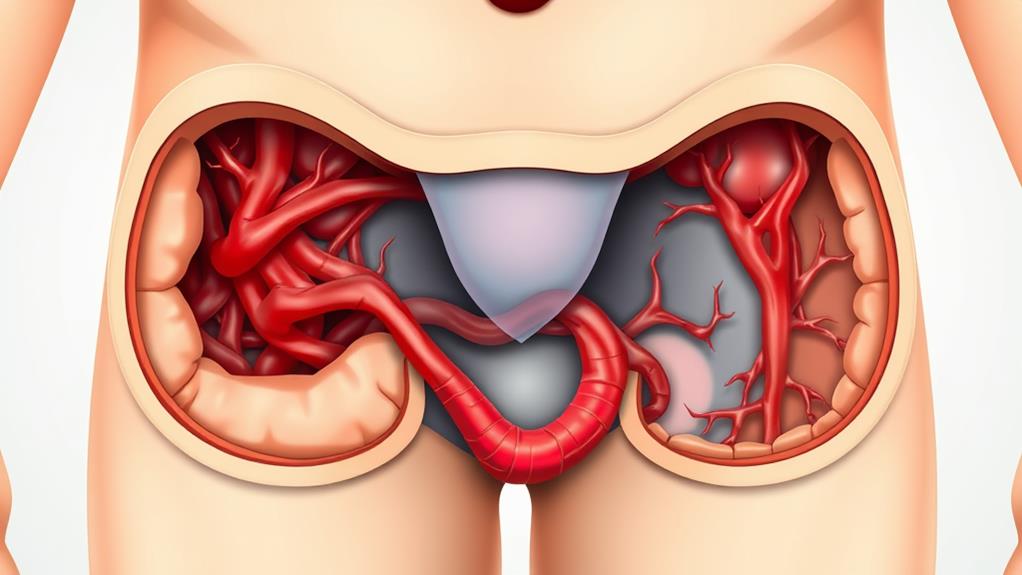
When you're dealing with internal hemorrhoids, you're facing a condition that's not immediately visible. These swollen blood vessels develop inside the rectum, typically starting about an inch above the anal opening. Unlike external hemorrhoids, which form under the skin around the anus, internal hemorrhoids aren't easily seen or felt.
The location of internal hemorrhoids within the rectum means they're often painless, as this area lacks pain-sensitive nerve endings. However, they can cause discomfort and other symptoms:
- Bleeding during bowel movements
- A feeling of fullness or pressure in the rectum
- Mucus discharge
- Prolapse (hemorrhoid tissue protruding from the anus)
- Itching or irritation in the anal area
In terms of appearance, internal hemorrhoids aren't typically visible unless they prolapse. When this happens, you might see or feel a soft, pink mass protruding from the anus. The size can vary from a small grape to a larger lump. Bear in mind that while external hemorrhoids often appear as a visible bump or lump, internal hemorrhoids remain hidden unless they prolapse or are examined by a healthcare professional using specialized tools.
Common Symptoms
While the location of internal hemorrhoids makes them less visible, they still present distinct symptoms that can alert you to their presence. One of the most common signs is rectal bleeding, which you might notice as bright red blood on your toilet paper or in the toilet bowl after a bowel movement. Worth mentioning is that while this symptom can be alarming, internal hemorrhoids are usually painless.
Another symptom you might experience is the sensation of something protruding from your anus during bowel movements. This occurs when internal hemorrhoids prolapse, potentially causing discomfort, itching, and irritation around the anal area. You may also notice mucus discharge, which can contribute to the itching sensation.
If left untreated, internal hemorrhoids can lead to more severe complications. Chronic blood loss may result in anemia, while strangulation can cause intense pain and potentially life-threatening issues. To prevent hemorrhoids from worsening, it is vital to address these symptoms early. Remember, while internal hemorrhoids share some symptoms with other conditions like anal fissures, they're typically painless unless complications arise. If you're experiencing persistent rectal bleeding or other concerning symptoms, consult your healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Treatment Options Available
Treatment options for internal hemorrhoids vary depending on their severity and the associated symptoms. Your doctor may recommend conservative measures like sitz baths, fiber supplements, or Witch hazel applications for mild cases. However, if these don't provide relief, you might need medical procedures.
Here are some common treatment options for internal hemorrhoids:
- Rubber band ligation
- Infrared coagulation
- Sclerotherapy
- Hemorrhoidectomy
- Lifestyle changes
Rubber band ligation is a popular office-based procedure where a small rubber band is placed around the base of the hemorrhoid, cutting off its blood supply. This causes the hemorrhoid to shrink and eventually fall off. For smaller hemorrhoids, your doctor might suggest infrared coagulation, which uses heat to shrink the tissue, or sclerotherapy, involving chemical injections.
In severe cases that don't respond to other treatments, hemorrhoidectomy might be necessary. This surgical procedure removes the hemorrhoid tissue entirely. It's typically reserved for Grade Four hemorrhoids that can't be pushed back into the anal opening.
External Hemorrhoids Overview
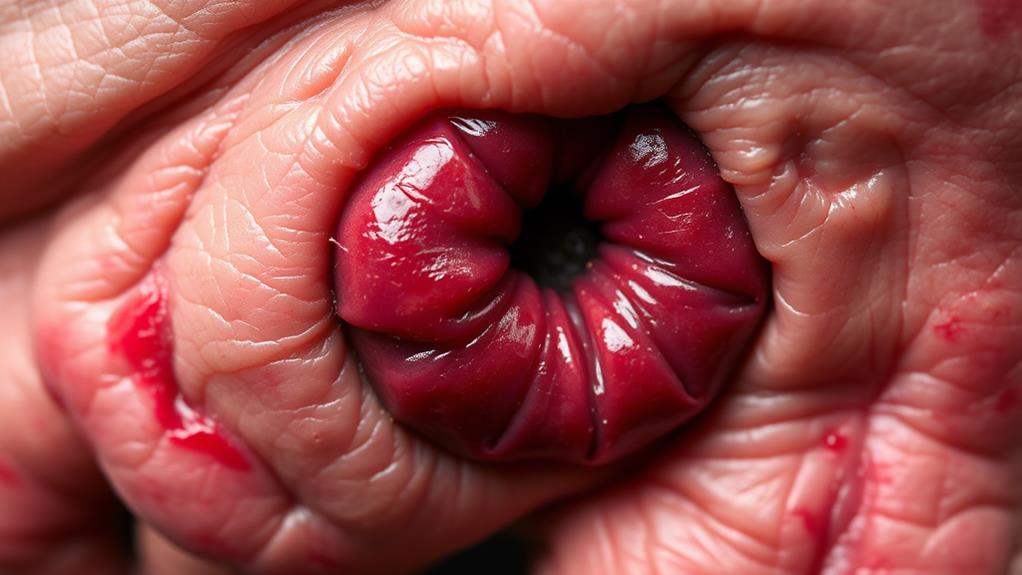
Located just beneath the skin surrounding the anus, external hemorrhoids can be a source of significant discomfort. You'll often notice a lump near your anus, which may be tender to touch and cause pain, especially during bowel movements. These swollen blood vessels can become extremely painful if they develop a blood clot, known as a thrombosed external hemorrhoid.
External hemorrhoids typically present with symptoms like itching, pain, and bleeding. You might notice bright red blood on toilet paper or in your stool after a bowel movement. The skin around your anus may also feel irritated or uncomfortable. In some cases, you may experience a constant ache or burning sensation in the affected area.
If you're dealing with external hemorrhoids, several treatment options are available. Start with self-care measures like warm baths, ice packs, and over-the-counter creams. These can help reduce swelling and alleviate discomfort. However, if your symptoms persist or worsen, it's vital to consult a healthcare professional. They may recommend more aggressive treatments, including surgical removal in severe cases, to restore proper blood flow and relieve your hemorrhoid symptoms.
Distinguishing Symptoms
You'll notice distinct differences in pain and discomfort between internal and external hemorrhoids. While external hemorrhoids often cause sharp pain and sensitivity, internal hemorrhoids typically don't cause pain unless they prolapse. Bleeding patterns also differ, with external hemorrhoids more likely to cause visible blood on toilet paper, while internal hemorrhoids may lead to blood in the toilet bowl.
Pain and Discomfort Differences
Pain and discomfort are often key indicators in distinguishing between internal and external hemorrhoids. Internal hemorrhoids rarely cause significant discomfort, as they're located inside your rectum where there are fewer pain-sensing nerves. You might experience mild discomfort or a feeling of fullness, but severe pain is uncommon. External hemorrhoids, however, can result in pain and irritation around the anus due to their location on sensitive skin.
Here's a quick comparison of pain and discomfort differences:
- Internal hemorrhoids: Rarely cause pain unless they prolapse
- External hemorrhoids: Can cause extreme discomfort, especially when sitting
- Thrombosed hemorrhoid: May cause intense, throbbing pain
- Mixed hemorrhoids: Symptoms vary depending on location
- Chronic hemorrhoids: Discomfort may increase over time
If you're experiencing persistent pain or your symptoms get worse, it's vital to consult a healthcare provider. They can determine whether you have internal or external hemorrhoids and recommend appropriate treatment. Remember, while both types can cause discomfort, external hemorrhoids are more likely to result in noticeable pain. Early intervention can prevent complications and provide relief from hemorrhoid-related discomfort.
Bleeding Patterns Comparison
Bleeding patterns can be a key indicator in differentiating between internal and external hemorrhoids. While both types can cause bleeding, the way you might notice it differs. Internal hemorrhoids often result in bright red blood in the toilet bowl or on toilet paper after a bowel movement. You might not see or feel these hemorrhoids, as they're located inside the rectum. External hemorrhoids, on the other hand, are visible outside the anus and can cause blood to pool in an external sac.
Here's a comparison of bleeding patterns for internal and external hemorrhoids:
| Characteristic | Internal Hemorrhoids | External Hemorrhoids |
|---|---|---|
| Blood Color | Bright red | Dark red |
| Visibility | Not visible | Visible outside anus |
| Amount | Small amount | Can be substantial |
| Location | In toilet bowl | On tissue or clothes |
It's important to note that not all hemorrhoids bleed, and bleeding can indicate other conditions. If you experience persistent bleeding, consult a doctor for a proper diagnosis. They may perform a rectal exam to determine the type and severity of your symptomatic hemorrhoids and recommend appropriate treatment based on the blood supply and location of the affected area.
Common Causes and Risk Factors
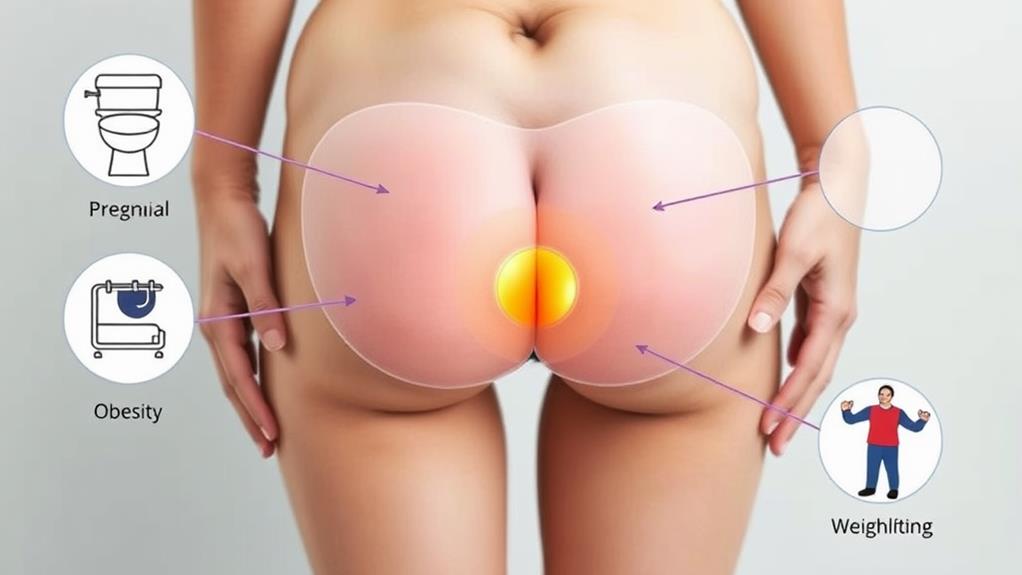
Hemorrhoids frequently develop due to a combination of factors that increase pressure on the veins in the rectum and anus. You can prevent hemorrhoids by addressing common causes and risk factors. Constipation and chronic diarrhea are major contributors, as they lead to straining during bowel movements. This excessive pressure can cause veins to swell, potentially resulting in large external hemorrhoids.
Your diet plays a vital role in preventing hemorrhoids. A low-fiber diet often leads to hard stools, which increase the risk of constipation and straining. Obesity also puts extra pressure on your rectal and anal veins, making you more susceptible to hemorrhoids.
Chronic constipation or diarrhea
Pregnancy
Low-fiber, high-processed food diet
Obesity
Prolonged sitting, especially on the toilet
During pregnancy, hormonal changes and increased pressure on your rectal and anal veins can cause hemorrhoids. If you have a desk job or spend long periods sitting, you're also at higher risk due to decreased blood flow and increased pressure in the area. By addressing these factors, you can substantially reduce your chances of developing hemorrhoids.
Diagnosis Methods
Your doctor's first step in diagnosing hemorrhoids typically involves a thorough discussion of your symptoms and medical history. They'll ask about your bowel habits, any pain or bleeding you've experienced, and any family history of similar issues. Make an appointment if you suspect you have hemorrhoids, as early diagnosis can lead to more effective treatment.
During the physical exam, your doctor will visually inspect the anal area to determine if you have either internal or external hemorrhoids. They may also perform a digital rectal exam, inserting a gloved finger into your rectum to feel for abnormalities. In some cases, a more thorough examination called a flexible sigmoidoscopy may be necessary. This procedure uses a lighted tube to view the lower part of your colon and rectum.
If your symptoms are severe or don't improve with initial treatments, your doctor may refer you to a specialist, such as the American Society of Colon and Rectal Surgeons. These experts can help determine the difference between hemorrhoids and other conditions, like colorectal cancer, ensuring you receive the most appropriate care for your anal and rectal health.
Treatment Options
Once your doctor has diagnosed hemorrhoids, they'll recommend appropriate treatment options based on the severity and type of your condition. For internal hemorrhoids, several non-surgical treatments are available:
- Rubber band ligation: A small rubber band is placed around the hemorrhoid's base, cutting off blood supply and causing it to shrink.
- Infrared coagulation: Uses infrared light to heat and shrink the hemorrhoid.
- Sclerotherapy: A chemical solution is injected into the hemorrhoid to reduce its size.
These treatments are effective for most internal hemorrhoids, but severe cases may require surgical intervention. Hemorrhoidectomy, a surgical treatment option, involves removing the hemorrhoid under general anesthesia. It's used for both internal and external hemorrhoids when other treatments haven't been successful.
For external hemorrhoids, office treatment is often the first line of defense. This may involve lancing a thrombosed hemorrhoid to drain the blood clot, providing immediate pain relief. In some cases, surgical excision of the external hemorrhoid may be necessary.
Your doctor will help you choose the most appropriate treatment option based on your specific situation, considering factors such as the type, severity, and location of your hemorrhoids.
Prevention Strategies
Five key strategies can help prevent hemorrhoids from developing or recurring. First, focus on maintaining a high-fiber diet rich in whole grains, fruits, and vegetables. Aim to consume at least 25-30 grams of fiber per day to soften your stool and reduce straining during bowel movements. Second, drink plenty of water throughout the day to prevent constipation and keep your digestive system running smoothly.
Third, exercise regularly and maintain a healthy weight to reduce pressure on the veins in your rectum and anus. This can substantially lower your risk of developing hemorrhoids. Fourth, avoid prolonged sitting and take regular breaks to stretch and move around. This simple habit can help alleviate pressure on your rectal area.
Lastly, practice good bowel habits. Don't ignore the urge to use the bathroom, and avoid straining during bowel movements. When you do use the toilet, don't spend excessive time sitting there. By implementing these prevention strategies, you'll dramatically reduce your chances of developing hemorrhoids and minimize symptoms if you already have them.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Do I Know if My Hemorrhoid Is Internal or External?
You can identify your hemorrhoid type by its location and symptoms. Internal ones cause painless rectal bleeding during bowel movements. External ones cause pain, itching, and a visible lump near your anus. Consult a doctor for a proper diagnosis.
How Do You Fix Internal and External Hemorrhoids?
Imagine your body as a garden: to heal hemorrhoids, tend it with care. You'll find relief through natural remedies, home treatments, and quick fixes. Try hemorrhoid creams, witch hazel, cold compresses, sitz baths, and dietary changes. Surgery's a last resort.
Which Is Worse, Internal or External Hemorrhoids?
Your pain threshold and severity levels can make either hemorrhoid type worse. External hemorrhoids often cause sudden onset of unpleasant surprises, while internal ones pose hidden dangers like bleeding risks. Anorectal differences can lead to chronic suffering with both types.
Can Internal Hemorrhoids Self Resolve?
While you might fear they'll persist, internal hemorrhoids can self-resolve. Your pain threshold and the hemorrhoid's size affect healing rates. Natural remedies, lifestyle changes, and avoiding dietary triggers can prevent prolapse and recurrence. Be patient; duration varies.
Conclusion
You're now armed with an arsenal of knowledge to battle the dreaded hemorrhoid menace! Whether they're lurking inside or ambushing you from the outside, you've got the power to identify, treat, and prevent these pesky invaders. Don't let these tiny terrors rule your life! With the right strategies, you'll send hemorrhoids packing and reclaim your throne. Remember, your bottom's comfort is your top priority!
Amazon and the Amazon logo are trademarks of Amazon.com, Inc, or its affiliates.